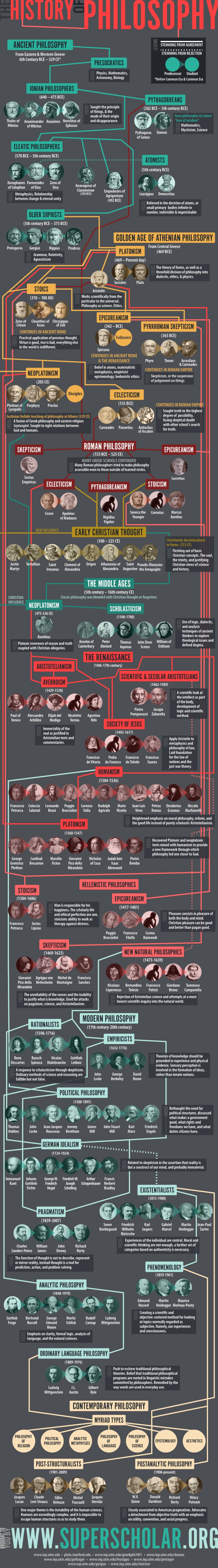
Western Philosophy Timeline
Note: These are still a Work In Progress. Some cleanup required.
Ancient Philosophy
Pre-socratic
Thales of Miletus
- Often referred to as the Father of Science
- Idea: Everything in the world is made out of water
- Ionian
Anaximander of Miletus
- Student of Thales
- He said there is something even more basic than water that the world is made of. He called it "unbound / limitless"
- Ionian
Heraclitus
- Ionian
- World is always in flux - it is "becoming"
Pythagoras
- He had a cult of followers
- World is the result of mathematics
Parmenides
- Eleatics(Region in Italy)
- World is stable or whole
Zeno
- Student of Parmenides
Democritus
- Atomic theory - everything is made of atoms
Protagoras
- He was a Sophist. Its a school of philosophy that taught people(for a price) how to argue. They were not held in high regard, as the idea was to win the argument rather than to find the truth. But the context of this teaching was to argue your case at a court hearing.
- Relativism: "Man is the measure of all things"
Socratic
- Socrates
- Plato
- Aristotle: Philosophy as science. Ethics.
- Epicurus: Belief in atoms, empiricist epistemology, hedonistic ethics.
- Phyro: Skepticism.
Roman
Focus was to try to make philosophy more accessible outside of an educated elite.
Cicero
Stoicism
Even though stoicism was created by greeks like Zeno of Citium and Chrysippus of Soli, it was developed on by later roman philosophers who were more influential...
Seneca
Epictetus
Marcus Aurelius
Apostolic
Mostly worked on christian concepts: Soul, Trinity, Christian views of science and history.
Saint Augustine
- Was originally a Manechian(another religion)
- But then he encountered Neo-platonism: A new version of Plato that has its issues solved using ideas from Christianity
- Wrote the book 'The Confessions'
- Created the idea of Original Sin
- Reason(aided by divine illumination) vs Desire
Middle Ages
Classic philosophy mixed with christian thought(or forgotten)
Neoplatonism
Boethius
- Translated works of Aristotle
- Worked to marry platonic reverence of reason and truth with christian stories.
Scholasticism
Used logic, dialectic and analysis to explore theological issues and defend christian dogma.
St Anselm of Canterbury
- Made the Ontological Argument for God
- "Faith seeking understanding"
Thomas Aquinas
- Proponent of Naturalism: Nature and its laws are not divine. They have logical relationships and can be understood through investigation.
- Believed in Virtue Ethics
William of Ockham
- Ockham's Razor is (mis)attributed to him
Renaissance
Ibn Sina / Avicenna (930 AD - 1037 AD)
- Neoplatonist
- He combined Islamic theology with naturalism
Averroes
- Islamic Philosopher
Niccolo Machiavelli
- Wrote: The Prince
Copernicus
Rejection of Aristotelian science, scientific inquiry into the natural world.
Modern
Rationalists
View scholasticism through skepticism. Methods of science are fallible - but not false. Focus on reason above senses.
Rene Descartes
- Created the Cartesian Coordinate system
- "I think, therefore I am"
- Dualism
- Realm of mind and Realm of body
- He proposed the scientific method
- Question everything that's not self evident
- Divide everything into smallest, simplest parts
- Solve problems going from simplest to most complex
- Re-examine the reasoning
Spinoza
- Rationalist
- Everything that exist is a part of the God(of judism)
Blaise Pascal
- Mathematician
- He maintained that faith is more important than reason to gain knowledge
Leibniz
- Everything is created from monads
Empiricists
Knowledge should be grounded in experience and physical evidence. Focused on experience gained by senses.
Francis Bacon
- Defended the interconnectivity of Philosophy, Politics and Science
- Ethical life is one led by reason and logic
- He created Inductive Reasoning: Going from Specific understanding to general.
- Deductive goes from general understanding to specific.
- Focused on Falsifiability
Thomas Hobbes
- The only universal things are names themselves
- Everything is material
John Locke
- Tabula Rasa(everyone's mind starts as an clean slate)
- We learn everything
- Ethical/civil behavior should be guided by natural laws
David Hume
- Emotions were given higher priority to Reason
- We should try to increase pleasure and minimize pain
Political Philosophy
Political structures, systems of government, duties of citizens, rights and freedoms.
Thomas Hobbes
- Social Contract
Rousseau
John Stuart Mill
- Naturalist
- Minds and knowledge belong to the natural world
Karl Marx
German Idealism
Immanuel Kant
Hegel
Arthur Schopenhauer(1788-1860)
- He agreed with principle of sufficient reason
- But its was not enough - there is a will that drives things
Pragmatism
- Charles Sanders Peirce
- William James
- Richard Rorty
John Dewey(1859-1952)
- Democracy/political theory
- Learning in a social process that has 'radical empiricism'
- We regulate actions and perspective according to our own experience - But also by interactions with other
- Gender as a social construct
Existentialism
- Soren Kierkegaard
- Friedrich Nietzsche
- Heidegger
- Jean-Paul Sartre
Karl Jaspers
- Psychiatrist
- Science cannot deal with topics of mind and spirit - We need a leap of faith
- Denounced technocratic governments
- Technology advances faster than our understanding of it - and this creates an unstable system
Continental Philosophy
- Spirit of Romanticism
- Aligned with social revolutions
- Focus on Individuals
Max Morkheimer
- Traditional Theory
- Control and manipulation of nature
- Theories/Hypothesis
- Impartiality/Objectivity
- Controlled by the dominant ideology
- Critical Theory
- Critical Thinking
- Relatated to the current culture
- Subjectivity has a big role
- Subject and Theory cannot be divorced from the historical influence
Ralph Waldo Emerson(1803-1882)
- Self improvement
- Human life, Nature, Divinity are all part of the same system
- All truths are within and nothing external is needed
Henry David Thoreau
- Focused on the simple individual life
- Environmentalism
- Influenced Anarchical thought
Analytical Philosophy
- Focus on Science/Empiricism
- Industrial Revolution
- Focus on Darwinism
- Emphasis on clarity, formal logic, natural sciences
Bertrand Russel
Auguste Comte
- Responsible for establishing the social sciences and the philosophy of science
- Positivism
- Theological and Metaphysical method are inherently flawed
- Only Natural phenomena can give positive knowledge thru empirical methods
- Social sciences can help us to study society empirically
Herbert Spence(1820-1903)
- Coined the phrase "Survival of the fittest"
- Tried to create a fully naturalized utilitarian theory
- Natural selection -> ethics gets better over time
- Had some elements of Eugenics
George Boole
- Moved towards a Logical system that was objective and practical
- Created Boolean Logic
- Created Propositional Logic
Edmund Gettier(1927-2021)
- Knowledge is Justified True Belief (Epistemology)
- But there is problems with this view - Gettier problems
Hilary Putnam
- Death of Ontology
- Conceptual Relativity - Anti-metaphysical linguistic perspective of epistemology
George Moore
- Meta ethics
- Good actions can only be assessed by intuition(way to obtain direct and simple knowledge)
- Moral good should be seen within the context of the action
- Not as a individual component
- But as the whole action
Richard Hare
- Utilitarian Perspective
- Universalizable
- Normative words(good/ought) are similar to a logical operator directed to everyone
- Prescriptive
- Suggests a model of action in given situations("one shall not kill")
- Supervenience/Overriding
- Moral Properties arise from non-moral ones and are representable by a general ethical guidance
- Universalizable
Bernard Williams
Critical of attempts to create ethical norms - Moral life cannot have universal patterns or rules
- Thick Ethical Terms: Proper factual association - eg. Courage, lie, brutality
- Thin Ethical terms: Weak terms that is subjective/variable. Eg. right, bad, ought
Morality relates to the linguistics used in a community
Gertrude Margaret Anscombe
- Later denounced Consequentialism
- Focused on Intention
Philippa Foot
- Focused on how morality takes place
- Criticized supremacy of rationality
- Compares morality to rules of etiquette
- Maintains the objectivity of morality
- Created the Trolly Problem
Ordinary Language Philosophy
Ludwig Wittgenstein
John L Austin
- Philosophy of Language
- Social and practical theory of meaning through "speech acts"
- Speech Acts: Speech is not just sound - its an action with meaning
- Language has 3 aspects
- Locutionary: Sounds and words
- Illocutionary: Meaning of the words
- Perlocutionary: Social impact of the words
Gilbert Ryle
Noam Chomsky
- Universal Grammar: All languages have...
- Nouns/verbs/articles + common grammar elements
- Similar sounds/vocalizations